8 Prokaryotes Lack Which of the Following Organelles
Although all prokaryote and eukaryote cells have cytoplasm or cytosol that contains several membrane-bound bodies. Prokaryotic cells lack organelles such as Golgi apparatus endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Prokaryotic Cells Article Khan Academy
E They lack membrane-bound nuclei.

. All of the above. The nucleus and the Golgi apparatus. Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack organelles or other internal membrane-bound structures.
A They have a semirigid cell wall. B They are motile by means of flagella. What is the advantage of prokaryotes with absence nucleus.
The absence of organelles in prokaryotes means that they cannot perform the function of photosynthesis. Prokaryotes do not have chloroplasts and mitochondria. Replicator molecules DNA or RNA.
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. C They possess 80S ribosomes. Prokaryotic cells lack which of the following.
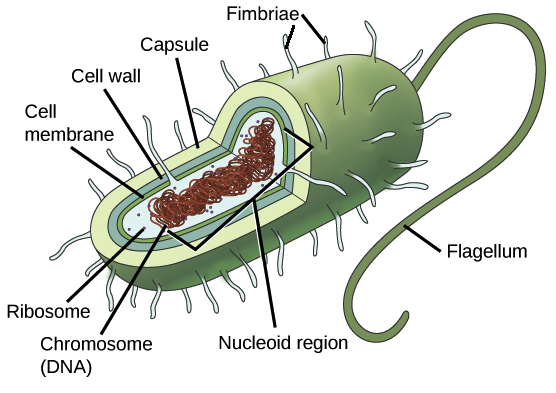
Prokaryotic Cell Diagram The prokaryotic cell diagram given below represents a bacterial cell. Which of the following organelles are enclosed by a double membrane. Prokaryotic lack which of the following.
Prokaryotes are divided into two distinct groups. Prokaryote cells lack the typical eukaryote organelles such as Golgi apparatus endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria and chloroplasts. What structures do they utilize for processes such as aerobic respiration and photosynthesis.
Prokaryotic organisms lack A. A prokaryotic cell lacks certain organelles like mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies. Prokaryotes lack a defined nucleus which is where DNA and RNA are stored in eukaryotic cells mitochondria ER golgi apparatus and so on.
Having no true nucleus has its own advantages. A piece of circular double-stranded DNA located in an area of the cell called the nucleoid. A cell membrane B.
All of the above. A nuclei and chloroplasts B mitochondria and chloroplasts. The lack of internal membranes means that prokaryotes cannot compartmentalize function to the same extent as eukaryotes.
Proteins are polymers of 20 molecules called. In addition to the lack of organelles prokaryotic cells also lack a cytoskeleton. The strongest evidence for the endosymbiotic origin of eukaryotic organelles is the similarity between extant prokaryotes and which of the following.
It suggests that the amount of DNA remains the same throughout the life cycle. The lack of organelles in prokaryotes means that they are structurally less complex than eukaryotes. Which of the following cell organelles is absent in prokaryotic cells.
What organelles are in Prokaryotes but arent in Eukaryotes. What organelle do prokaryotes lack. The lack of organelles in prokaryotes means that their basic cellular processes are different from eukaryotes.
Most prokaryotes have a cell wall outside the plasma. Which of the following statements about prokaryotic cells is generally false. All organelles are enclosed by a double membrane.
Therefore they do not have a nucleus but instead generally have a single chromosome. All of the above answer choices. Plasma membrane some have heterovysts filaments biofilms Compare the differences in shape volume of DNA and location of the genome of eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Some organelles that prokaryotes lack includes Golgi bodies and mitochondria. They obtain their nutrition from functional chloroplasts and each. D They reproduce by binary fission.
Diatoms lack any organelles that might have the 92 pattern. It depicts the absence of a true nucleus and the presence of a flagellum that differentiates it from a eukaryotic cell. All membrane function in prokaryotes is accomplished in the plasma membrane while in eukaryotes these functions are more.

Prokaryotic Cell Definition Examples Structure Biology Dictionary

Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Similarities Differences

Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes What Are The Key Differences Technology Networks

No comments for "8 Prokaryotes Lack Which of the Following Organelles"
Post a Comment